MIMICause: Representation and automatic extraction of causal relation types from clinical notes
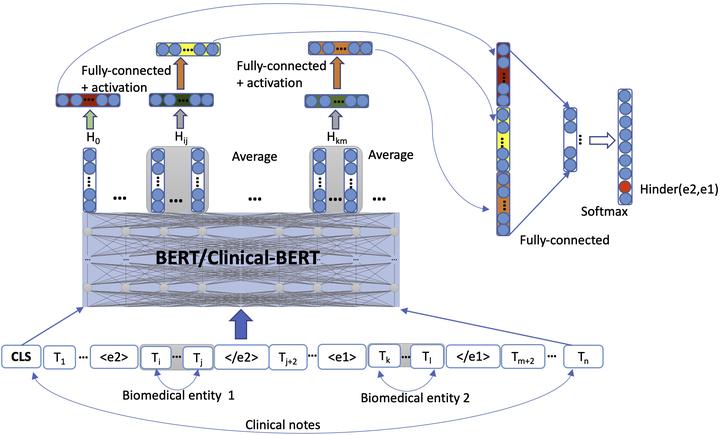 BERT/Clinical-BERT with entity context and FFN
BERT/Clinical-BERT with entity context and FFN
Abstract
Understanding causal narratives communicated in clinical notes can help make strides towards personalized healthcare. Extracted causal information from clinical notes can be combined with structured EHR data such as patients’ demographics, diagnoses, and medications. This will enhance healthcare providers’ ability to identify aspects of a patient’s story communicated in the clinical notes and help make more informed decisions.
In this work, we propose annotation guidelines, develop an annotated corpus and provide baseline scores to identify types and direction of causal relations between a pair of biomedical concepts in clinical notes; communicated implicitly or explicitly, identified either in a single sentence or across multiple sentences.
We annotate a total of 2714 de-identified examples sampled from the 2018 n2c2 shared task dataset and train four different language model based architectures. Annotation based on our guidelines achieved a high inter-annotator agreement i.e. Fleiss’ kappa ($\kappa$) score of 0.72, and our model for identification of causal relations achieved a macro F1 score of 0.56 on the test data. The high inter-annotator agreement for clinical text shows the quality of our annotation guidelines while the provided baseline F1 score sets the direction for future research towards understanding narratives in clinical texts.